AMTech...
Contents
- 1 PaaS
- 2 Thing
- 3 IoT
- 4 Edge
- 5 Big Data & Real time
- 6 The Challenge
- 7 IoT Core services
- 7.1 IoT Resources semantic
- 7.2 IoT Real Time View
- 7.3 Identity access management
- 7.4 Sensor Network
- 7.5 IoT Real Time Intelligence
- 7.6 Location-aware
- 7.7 Rules and Actions Execution
- 7.8 Push notifications
- 7.9 Time-aware
- 7.10 Scheduler Fault-tolerant distributed
- 7.11 Generating code and data binding
- 7.12 Observation Enrichment
- 7.13 Edge intelligence and M2M Bridge
- 7.14 Followers User Experience
- 7.15 Cloud App Marketplace
- 7.16 Electronic Product Code
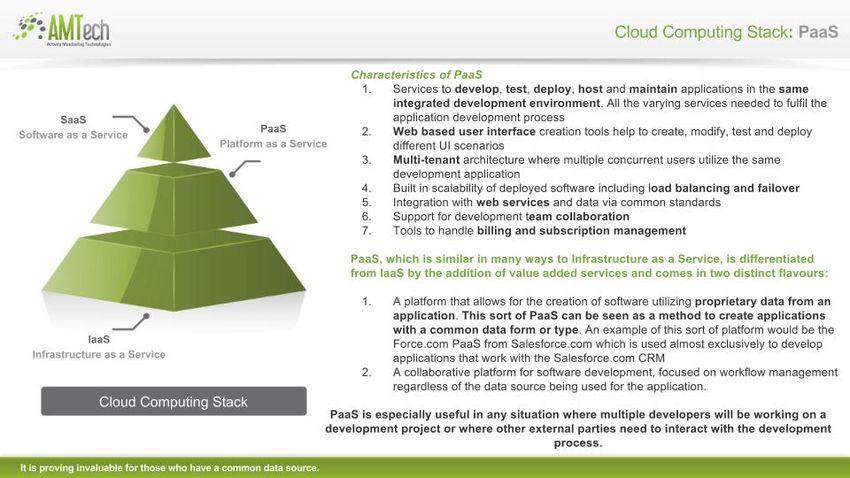
PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) brings the benefits that SaaS bought for applications, but over to the software development world. PaaS can be defined as a computing platform that allows the creation of web applications quickly and easily and without the complexity of buying and maintaining the software and infrastructure underneath it. PaaS is analogous to SaaS except that, rather than being software delivered over the web, it is a platform for the creation of software, delivered over the web.
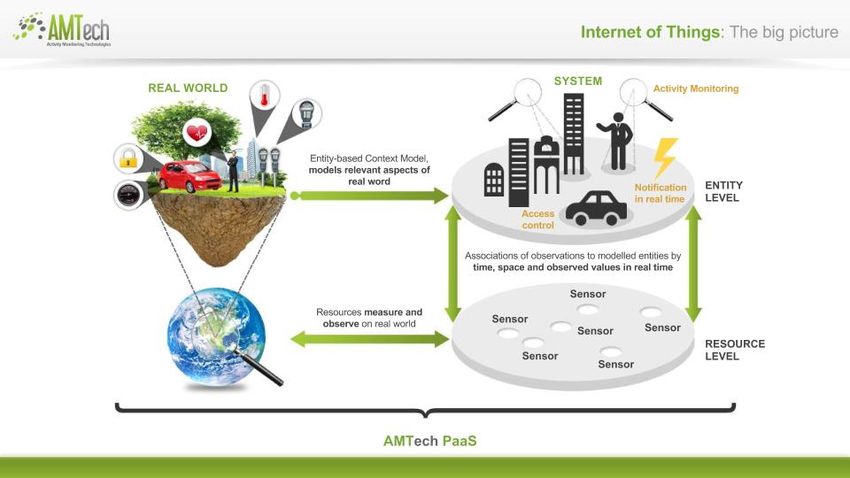
Thing
A Thing is a physical object or even a piece of data, with a unique identifier and a group of properties like: location, temperature, speed, acceleration, altitude, weight, volume, pressure, value or any other variable that can be measured
IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the network of physical objects (things) with unique identifiers and the ability to communicate and sense, as well as interact with their internal states and/or the external environment, without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction, by leveraging the Internet.
Edge
the edge could be the devices themselves, an on-premise gateway connecting a group of devices, or even a machine in the cloud. The right flavor will be dictated by the use cases, but in every situation there will be value in distributing intelligence to the edge
- Greater Responsiveness
- Lower Total Cost of Ownership
- Scalability
- Device Interoperability
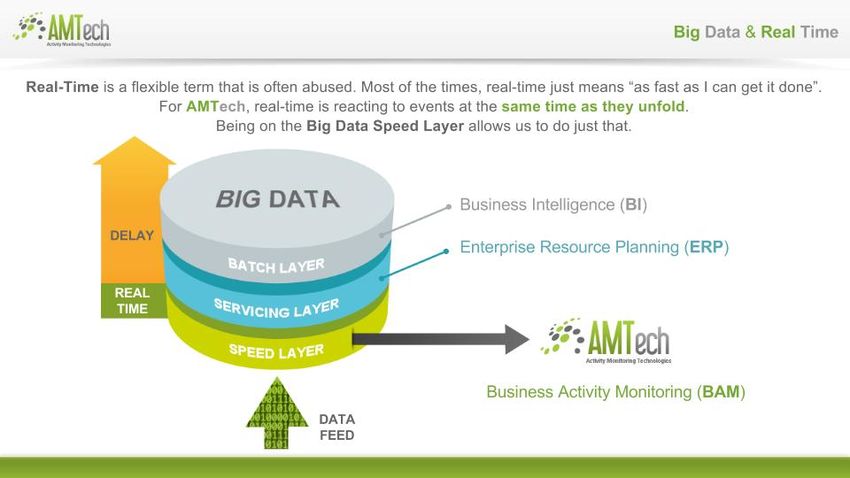
Big Data & Real time
The Challenge
IT encompasses a set of technologies, concepts and software stacks in order to use it to solve a problem in real time
Access control from the edge to the cloud
- Things, Data and Commands (See Resources)
- Configurable (Actors)
- Business rules
- Actions
- Integration with tenants and existing systems.
Devices (M2M)
- Devices Protocols
- Communication Protocols
- Centralized management
- Edge intelligence
- Monitoring
Cloud based & multitenancy
- multitenant
- scalable on-demand
- Big Data
- streaming in real time
Reasoning in real time
Extensible API
- Things type, Observations type and Commands
- Observation enrichment
- Placeholders
- M2M Bridge
Location Systems
- GIS
- Proximity area
- Positioning systems
Acting in real time
Applications evolution
Reference data
Example of what developers think Stay of IoT
IoT Core services
- A service refers to a set of related software functionalities that can be reused for different purposes, together with the policies that should control its usage
IoT Resources semantic
- Restful and NOSQL real-time views; for querying and managing resources semantic; structured according to the RDF and represented leveraging linked data and Json-ld.
- Supports resources types version control with publication policies
IoT Real Time View
- Restful and NOSQL real-time view for querying and managing resources instances; structured according to the RDF and represented leveraging linked data and Json-ld.
- Support instances enrichment, allowing insert new properties and values after semantic been extended.
Identity access management
- Manages the identity and information of users that describes the operations and access control over IoT resources, offering a secure multi-tenancy and protected IoT real time view data hosting.
- actors for grouping access policies
- access control based on resource’s type, tenant and user id
Sensor Network
- Restful publish / subscribe message broker and event processing network that allows subscribers and publishers to exchange observations classified by topics or/and observations types; uses linked data to represent observations semantic and MQTT topics to express the physical organization of sensors network.
IoT Real Time Intelligence
- Query engine for discovering new knowledge emerging from associating real time observations with Things real time views, bringing into account time, spatial location and observed properties.
Location-aware
- Set of geometric and mathematical algorithms responsible for the location, organization and spatial relation between Things. It leverages geolocation/GPS or WiFi positioning system and proximity location technologies to guarantee that observations and things get enriched with accurate location.
Rules and Actions Execution
- A distributed computation framework that offers the queuing and stream processing capabilities for computing IoT real-time views; by processing observations and executing pre-configured observers and actions.
Push notifications
- A service for sending asynchronous notifications using a private channel, leveraging access control policies, sensor network infrastructure and HTML5 websockets.
Time-aware
- Maintains a set of copies of observed properties per Thing; control by frequency and amount of copies; allows real time view data size and expiration time configuration.
Scheduler Fault-tolerant distributed
- is used to schedule tasks and orchestrate the executions of business rules actions.
Generating code and data binding
- For the creation and consumption of error free resources configuration information.
Observation Enrichment
- producer, access control topics and things relation can be configured to be enriched with:
- geospatial information like country, city...
- user content, user id, tenant…
- EPC information company prefix, product code..
- Other M2MBridge plugins placeholders
Edge intelligence and M2M Bridge
- Configurable edge intelligence
- Integrated devices and M2M protocols (data and commands from/to devices)
- SNMP, LLRP, iBeacon, eddystone, PLC, GPIO, EPC, NFC and many others domain protocols
- Device-to-device or device-to-cloud communications (connecting the devices to the cloud)
- LoRa, wifi, classic Bluetooth, BLE, Wi-Fi HaLow, ZigBee, Symphony Link, RFID, Wi-Fi Aware
- Remote and centralized control of IoT devices and gateways.
- Common functionality and host the execution of the protocols
- Network failure detection and recovery
- Get centralized configuration information at startup and real time modifications
- Access control policies to manager observations production and consumption
Followers User Experience
- access to things and notifications based on follower roles, tenant and user
- scale when new things, sensors and business rule get deployed
- dynamically associates monitored things and business rules without experiencing the “concept” of application
Cloud App Marketplace
- offers the tools for:
- developers to quicker and simpler deliver IoT solutions to market.
- businesses to discover new IoT solutions that extend your business.
Electronic Product Code
- encoding and decoding:
- SGTIN-96, SGTIN-198, SSCC-96, SGLN-96, SGLN-195, GRAI-96, GRAI-170, GSRN-96, GSRNP-96, GDTI-96, GDTI-174, GID-96.