Difference between revisions of "Edge reasoners"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Allows to configure reasoners to be executed by M2MBrigdes of an [[M2MBridge_network|M2MBridge Network]]. A reasoner consists of two fundamental parts: | Allows to configure reasoners to be executed by M2MBrigdes of an [[M2MBridge_network|M2MBridge Network]]. A reasoner consists of two fundamental parts: | ||
* An observer | * An observer | ||
| − | * A list of one or more actions | + | * A list of one or more actions to execute |
==Observer== | ==Observer== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[File:erBindingActionsProperties.png|950px|thumbnail|center|Select observation type]] | [[File:erBindingActionsProperties.png|950px|thumbnail|center|Select observation type]] | ||
| − | ===Custom | + | ===Custom action=== |
| − | + | A custom action is a very powerful tool that allows you to build an action for the execution of custom code in a controlled environment. Once you decide a name for the action you will be able to write a code based on the observation that was generated in the bridge and met the observer's filters. This code will be written in the scope of a function with the following signature: | |
| + | |||
| + | function(observation, context) { | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | The observation is a javascript object with all the properties of the observation that was received. The context will be explained in the next section. The function doesn't need to return any value and even if it's not explicitly specified, it's an async function. It means that in its evaluation is changed to <code>async function(observation, context) {...}</code> | ||
====Context==== | ====Context==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The context | ||
Revision as of 22:19, 18 August 2019
Contents
Edge Reasoners
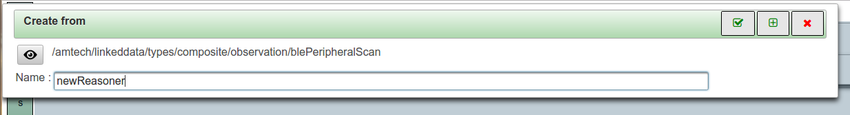
Allows to configure reasoners to be executed by M2MBrigdes of an M2MBridge Network. A reasoner consists of two fundamental parts:
- An observer
- A list of one or more actions to execute
Observer
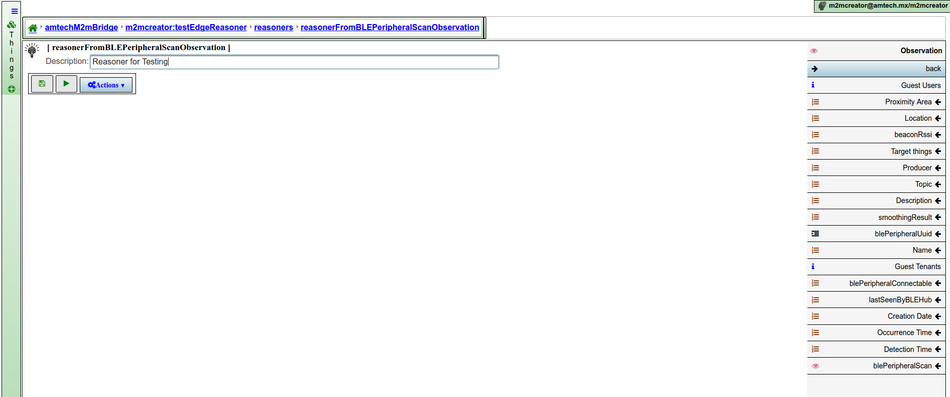
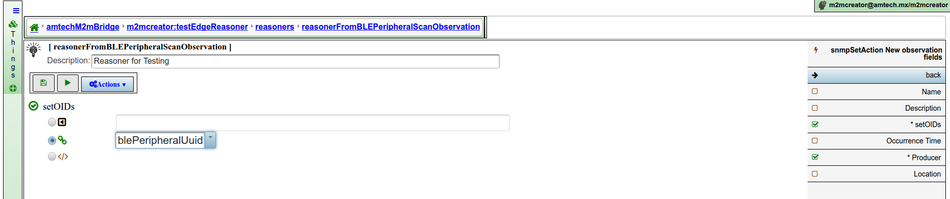
The observer is the conditional part. It's the condition that must be met in order to trigger the execution of actions associated to the reasoner. It starts by selection a type of observation among the types of observations configured in the observation production configuration of the bridge. When you decide to create a reasoner you will be asked for the type of observation that this reasoner will act on. Later on you will be allowed to also add constraints on this type of observation.
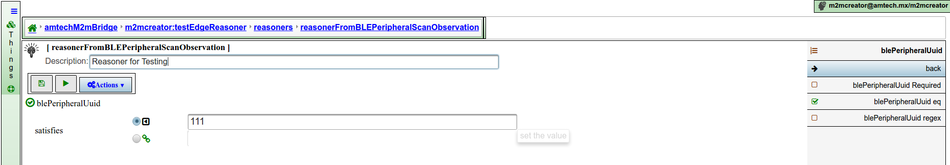
Constraints
The constraints that can be specified for the observer in an edge reasoner are very similar to those explained in this section. However, some kind of constraints are not allowed in this context. That's the case, for example, of proximity area based constraints. There are also some additions like isRequired, which is a new constraint that allows you to require the presence of a certain property in the observation.
Actions
Regarding actions you will be allowed to create two types of actions:
- Send command
- Custom action
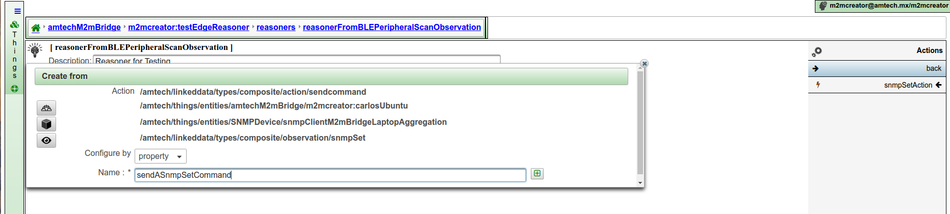
Send command
For the action send command you will be asked for several properties:
- The target M2MBridge instance
- The target plugin (thing instance) that will receive the command
- The command (observation type) to be sent
To fill the properties of the command to be sent, you will be able to specify bindings in a way that is very similar to the specification of bindings for cloud reasoners.
Custom action
A custom action is a very powerful tool that allows you to build an action for the execution of custom code in a controlled environment. Once you decide a name for the action you will be able to write a code based on the observation that was generated in the bridge and met the observer's filters. This code will be written in the scope of a function with the following signature:
function(observation, context) {
...
}
The observation is a javascript object with all the properties of the observation that was received. The context will be explained in the next section. The function doesn't need to return any value and even if it's not explicitly specified, it's an async function. It means that in its evaluation is changed to async function(observation, context) {...}
Context
The context