Difference between revisions of "Execution engine"
(→Security from the service) |
(→Security from the service) |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
Expected Behaviors | Expected Behaviors | ||
| − | * A follower that is not able to create/update/delete a resource of a certain type, because he does not have the actors, will be able to do so by pushing an observation that triggers a reasoner | + | * A follower that is not able to create/update/delete a resource of a certain type, because he does not have the actors, will be able to do so by pushing an observation that triggers a reasoner that does so. This will happen when the reasoner has the configuration for taking security from the service, and the follower is subscribed to the service. |
Check [[Access_control#Access_while_executing_observers_in_the_reasoner.27s_engine|this section]] for further details. | Check [[Access_control#Access_while_executing_observers_in_the_reasoner.27s_engine|this section]] for further details. | ||
Revision as of 14:57, 23 July 2018
Contents
CEP (Complex Event Processing — now called Event Stream Processing)
AMTech execution engine is an implementation of a CEP; it encapsulates CEP's complexity in the DAP design.
Execution feedback and/or errors
When an activity is being executed by the execution engine an observationlifecycle type is sent to the activity_lifecycle topic. Some events are reported through the property event, among this events:
- Start of a reasoner (BEGIN)
- End of a reasoner (END)
- Execution errors (ERROR)
The following example illustrates activity "producer": "thingsInBoardroom" reporting action "resourceuri": "/amtech/activities/thingsInBoardroom/reasoners/createThingInBoardroomFromEddystoneBeacon/actions/ReportThingInBoardroom" started "event": "BEGIN"
{
"topic": "/activity_lifecycle/thingsInBoardroom",
"guesttenants": [
"_ALL"
],
"event": "BEGIN",
"@type": "/amtech/linkeddata/types/composite/observation/observationlifecycle",
"producer": "thingsInBoardroom",
"resourceuri": "/amtech/activities/thingsInBoardroom/reasoners/createThingInBoardroomFromEddystoneBeacon/actions/ReportThingInBoardroom",
"detectiontime": "Tue Apr 26 21:41:09 UTC 2016",
"@id": "/amtech/things/observations/983c488f-c3d4-44ec-85f2-795428d12d83",
"occurrencetime": "Tue Apr 26 21:41:08 UTC 2016"
}
- This is a strong mechanism you can use to trace the execution of your activities if, at a given moment, you think they are not working as expected.
Security context
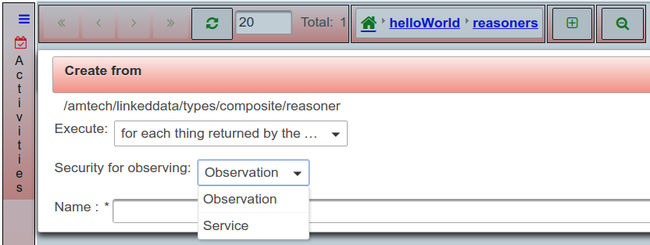
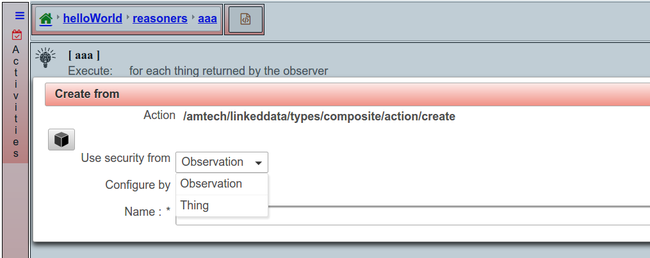
When creating a reasoner, the user can configure where will the security info will be taken from for executing the observer and performing the actions of the reasoners.
Security from the observation that triggers the reasoners
- The observer will return only things that belong to the tenant of the observation.
- Actions will be executed with the access rights of the user that sent the observation (access to types checked using user's actors and access to instances checked using the user's tenant)
- Actions that create resources (things, observations, notifications, etc) will initialize the security properties of the resource being created with the security info of the observation (ex. guest tenants)
Security from the service
THIS OPTION IS DISABLED AT THE MOMENT
- The observer will return all the things readable by the service (owned by the tenants or shared with them).
- Actions will be executed using the service (representing all tenants subscribed to the service)
- For actions that create resources in a reasoner of type Foreach, the user can configure the security info to be copied to the new resource. The security info can be taken from the observation or from the thing being iterated in the foreach
- Access policies to types are not enforced when executing actions. All actions performed by the topology will use the list of tenants subscribed to the service as only authorization info, so for accessing the resources, tenants and guest tenants will be checked against the list of tenants subscribed to the service, but types won't be checked since there is no info of actors available for a service.
Expected Behaviors
- A follower that is not able to create/update/delete a resource of a certain type, because he does not have the actors, will be able to do so by pushing an observation that triggers a reasoner that does so. This will happen when the reasoner has the configuration for taking security from the service, and the follower is subscribed to the service.
Check this section for further details.
Extension module
EPC
Electronic product code Tag Data Translation implemented according to the GS1 EPC Tag Data Translation 1.6 specification (http://www.gs1.org/epc/tag-data-translation-standard) Exposed as 2 JavaScript functions available for reasoner's JavaScript binding:
* epcEncode * epcDecode
They support the following codings:
- SGTIN-96, SGTIN-198, SSCC-96, SGLN-96, SGLN-195, GRAI-96, GRAI-170, GSRN-96, GSRNP-96, GDTI-96, GDTI-174, GID-96.
Debug
Geospatial libraries
A couple of libraries are available in JavaScript bindings:
You can make use of these libraries using the variables geolib and terraformer that are initialized as follows:
var geolib = require('geolib');
var terraformer = require('terraformer');
Example binding location property to a new created geofence thing, using the location from observation and calculating a circle with 300 radius
function(observation)
{
var location;
//get wkt json
var loc = JSON.parse(observation.location);
//parse longitude and latitude from wkt text
var point = terraformer.WKT.parse(loc.wkt);
//create a circle with 100 metres radius
var circle = new terraformer.Circle([point.coordinates[0], point.coordinates[1]], 100, 64);
//create location wkt
location = terraformer.WKT.convert(circle.geometry);
//wkt poligon location bind to created geofence thing
return location;
}