Difference between revisions of "Notifications"
From AMTech WikiDocs
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
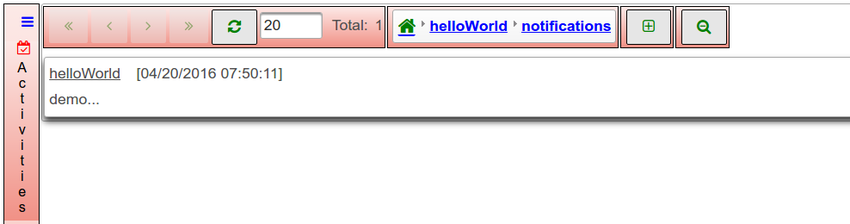
*A notification type is defined inside the activity | *A notification type is defined inside the activity | ||
[[File:notifications1.png|850px|thumbnail|center]] | [[File:notifications1.png|850px|thumbnail|center]] | ||
| + | ==Supported properties== | ||
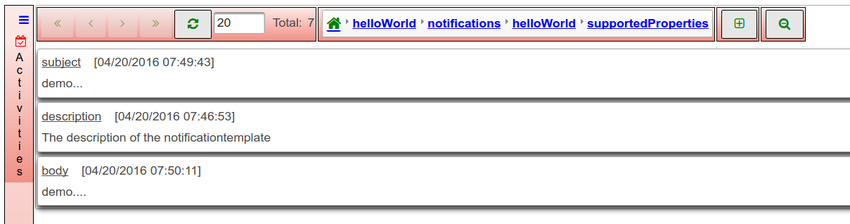
*A notification type has 3 supported properties | *A notification type has 3 supported properties | ||
[[File:notifications2.png|850px|thumbnail|center]] | [[File:notifications2.png|850px|thumbnail|center]] | ||
| − | + | ==Subject== | |
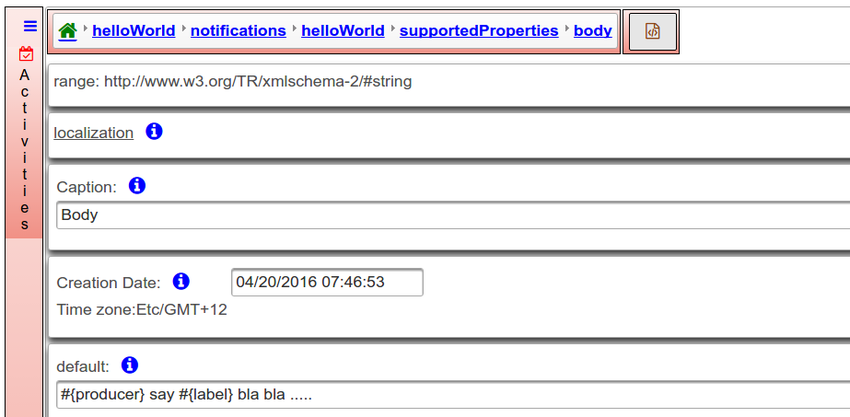
| + | Subject and body support placeholders #{placeholder-name}, to identify pieces of data to be replaced when a reasoner executes the notification action | ||
[[File:notifications3.png|850px|thumbnail|center]] | [[File:notifications3.png|850px|thumbnail|center]] | ||
| − | + | ==Binding values== | |
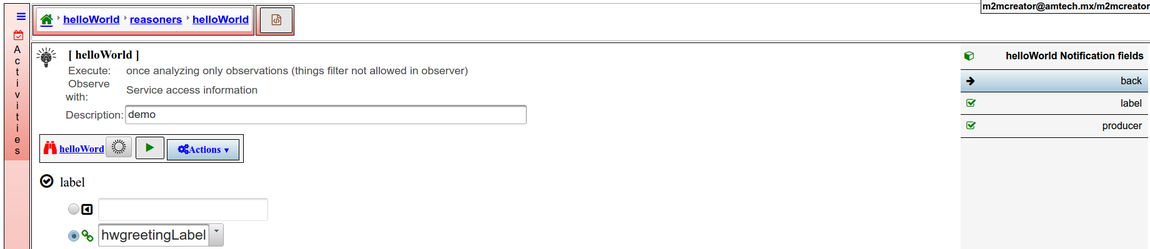
| + | Bindings to give values to the placeholders are defined in the activity actions | ||
[[File:notifications4.png|1150px|thumbnail|center]] | [[File:notifications4.png|1150px|thumbnail|center]] | ||
| − | + | ==Instances== | |
| + | Notification instances are generated when a reasoner with an action of type Notify is executed. Notification instances can be seen using the menu option Things->Notifications | ||
Revision as of 22:45, 13 May 2016
- A notification type is defined inside the activity
Supported properties
- A notification type has 3 supported properties
Subject
Subject and body support placeholders #{placeholder-name}, to identify pieces of data to be replaced when a reasoner executes the notification action
Binding values
Bindings to give values to the placeholders are defined in the activity actions
Instances
Notification instances are generated when a reasoner with an action of type Notify is executed. Notification instances can be seen using the menu option Things->Notifications